In the realm of financial management, rules-based money management plays a pivotal role in helping individuals and institutions make informed decisions and effectively manage their assets. In our previous discussion, we delved into the importance of establishing clear rules and guidelines to govern one’s financial strategy. In this continuation, we will explore the critical aspect of measuring the market within the context of rules-based money management.
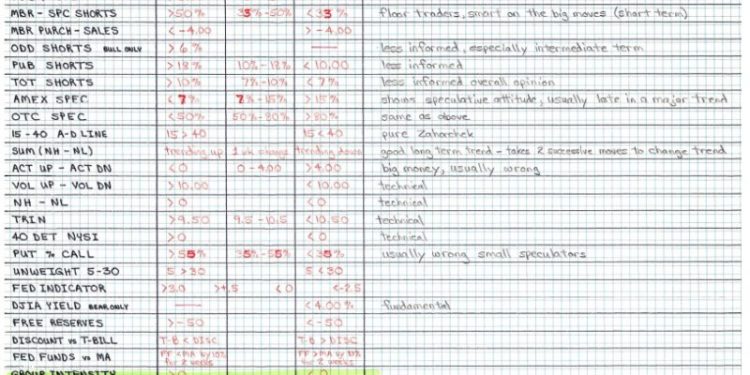
Market measurement serves as an indispensable tool for investors and managers to assess the overall health and performance of various financial instruments and markets. By evaluating key market indicators and trends, individuals can gain valuable insights that inform their investment decisions and guide their risk management strategies.
One of the fundamental metrics used in market measurement is the performance benchmark. Benchmarks provide a standard for comparison and help investors gauge the performance of their investments relative to a specified index or reference point. Common benchmarks include market indices such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, or Russell 2000. By measuring performance against a benchmark, investors can assess the effectiveness of their investment strategies and make adjustments as necessary.
Volatility is another crucial aspect of measuring the market. Volatility refers to the degree of fluctuation in the price of a financial instrument or market index over a specific period. High volatility indicates greater price fluctuations, while low volatility suggests more stable price movements. Understanding market volatility is essential for risk management, as it helps investors assess the level of uncertainty and potential downside risk associated with their investments.
Market breadth is another key measure that provides insight into the overall health and direction of the market. Market breadth refers to the number of individual stocks or securities advancing versus declining within a given market index. A strong market breadth, characterized by a higher number of advancing securities, is typically indicative of a healthy and robust market environment. Conversely, a weak market breadth, with more declining securities, may signal underlying weaknesses and potential bearish trends.
In addition to these metrics, technical analysis plays a vital role in market measurement within the context of rules-based money management. Technical analysis involves the evaluation of historical price data and market trends to forecast future price movements. By analyzing charts and using various technical indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD, investors can identify patterns and trends that inform their trading decisions.
In conclusion, measuring the market is a critical component of rules-based money management that empowers investors to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial markets effectively. By leveraging key metrics such as performance benchmarks, volatility, market breadth, and technical analysis, individuals can gain valuable insights that guide their investment strategies and risk management practices. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of market measurement is essential for building a solid foundation for successful financial management and wealth accumulation.